Into the wonderful world of ecosystems
What are ecosystems?
An ecosystem refers to a community of living organisms, together with their nonliving environment, that interacts and functions as a complex and interconnected network. This includes all parts from the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals, from the air, water, and soil to the sun and other sources of energy. Ecosystems can be found in virtually every part of the world, from the depths of the ocean to the highest peaks of mountains. They play a vital role in sustaining life on Earth.
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Visual%20(41).png)
Green Hermit, Phaethornis. A rare hummingbird from Costa Rica feeding on a flower.
The importance of ecosystems for human survival
Ecosystems are essential for human survival and wellbeing in many ways. They provide us with clean air and water, fertile soil for growing crops, and a rich variety of plant and animal life that we depend on for food, medicine, and other resources. They also regulate our climate, protect us from natural disasters, and support recreational activities, contributing to our physical and mental health. Without healthy and functioning ecosystems, human life as we know it would not be possible.
What is your impact on the environment? Calculate your carbon footprint.
Threats to ecosystems
Despite their crucial importance, ecosystems worldwide are under threat from various human activities. These include deforestation, pollution, overfishing, changing environmental conditions, and habitat destruction caused by urbanisation and development. These threats not only harm the environment and the creatures that inhabit it, but also have significant consequences for human health, the economy, and security.
Addressing these threats and protecting ecosystems for future generations is a crucial priority requiring global cooperation and action. Green Earth is dedicated to mitigating these threats through our projects and helping ecosystems prosper.
Read more: Beyond tonnes: How carbon credit co-benefits elevate value
Types of ecosystems
-1.jpg?width=1200&height=680&name=Frame%201%20(1)-1.jpg)
Terrestrial ecosystems
Terrestrial ecosystems are those that exist on land and include a wide variety of environments, from deserts and grasslands to forests and tundra. These ecosystems are home to countless species of plants and animals and play a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate and sustaining life. Terrestrial ecosystems are also important for human wellbeing, as they provide us with food, water, and other natural resources. However, they are vulnerable to threats such as deforestation, overgrazing, and changing environmental conditions, which can significantly impact their health and functioning.
Read more: Peatland restoration: Why it's crucial and how to pay for it
Aquatic ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems are those that exist in water and include everything from oceans and lakes to rivers and wetlands. These ecosystems are home to a vast array of aquatic organisms, from tiny plankton to large whales. They are vital for regulating the Earth's climate and supporting human life. They also play essential roles in the water cycle, nutrient cycling, and carbon storage. However, aquatic ecosystems are also threatened by pollution, overfishing, and changing environmental conditions, which can significantly impact the health and functioning of these ecosystems.
Read more: Marine ecosystems conservation
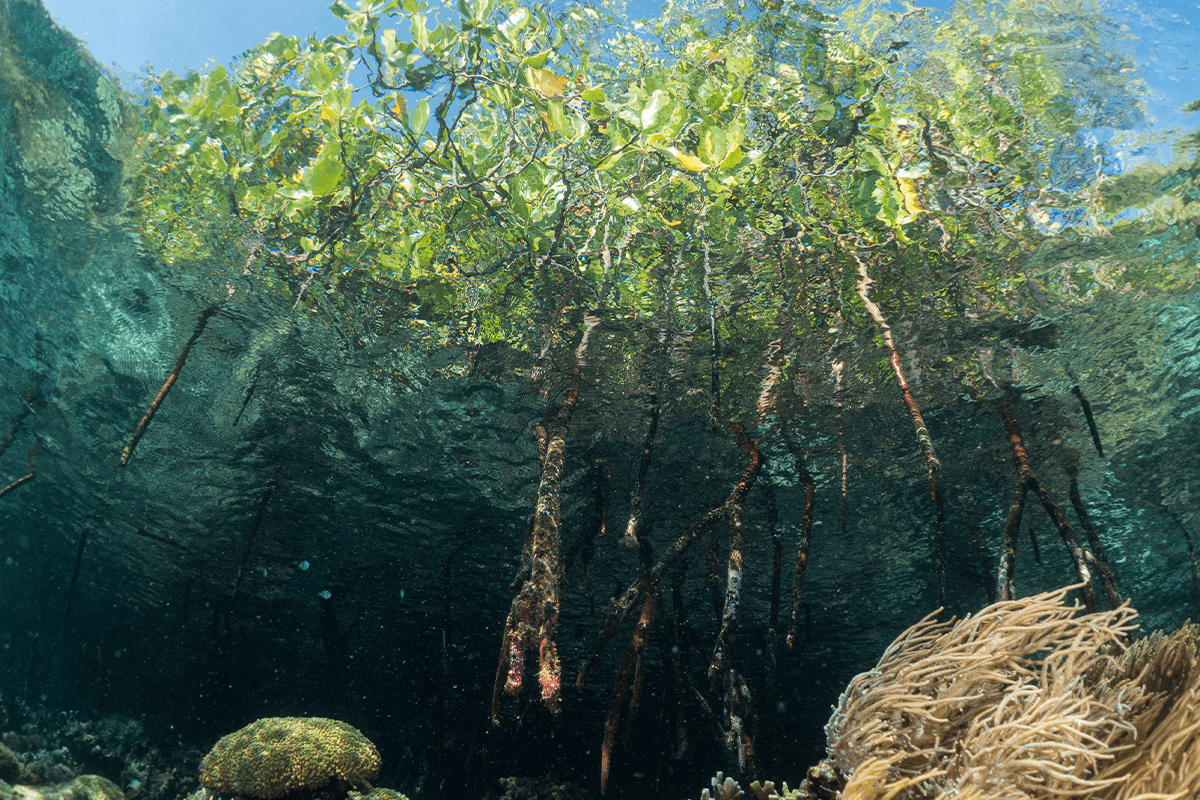

Flora and fauna at Raja Ampat Island, Indonesia.
Other types of ecosystems
In addition to terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, there are also other types of ecosystems that exist in more specialised environments. These include polar ecosystems, found in the Arctic and Antarctic regions and characterised by extreme cold and darkness; desert ecosystems, found in hot and arid regions and home to specialised plants and animals adapted to survive in harsh conditions; and urban ecosystems, found in cities and shaped by human activities such as construction, transportation, and waste disposal. Each of these ecosystems has its own unique characteristics and challenges and requires specialised approaches to conservation and management.
Read more: The ecosystems of Africa
Integrate trees into your business
We can help your company become more sustainable by integrating trees into your business.
Biodiversity in ecosystems
What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms existing within a particular ecosystem, as well as the variety of habitats, ecosystems, and ecological processes that support and sustain life. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems and is a critical component of healthy and functioning ecosystems.
The importance of biodiversity in ecosystems
Biodiversity is essential for ecosystems' health and good functioning, as it contributes to many ecosystem services that are vital for human wellbeing. Biodiversity helps maintain the quality of air, water, and soil. It supports the pollination of crops, the control of pests and diseases, and the production of food, fuel, and other resources. Biodiversity also plays a key role in regulating the Earth's climate and mitigating the impacts of natural disasters. In other words, biodiversity is the cornerstone of ecosystem health and sustainability and is indispensable for human survival.
Find out more about biodiversity offsetting
Threats to biodiversity
Unfortunately, biodiversity is under threat from a variety of human activities, including habitat destruction (such as deforestation), pollution, overexploitation, environmental instability, and the introduction of invasive species. These threats can significantly impact the health and functioning of ecosystems and lead to the loss of species, genetic diversity, and ecosystem services. The loss of biodiversity also has significant consequences for human health, the economy, and security. Addressing these threats and protecting biodiversity is therefore a crucial priority that requires global cooperation and action.
Read more: How biodiversity loss impacts ecosystems and what we can do to help
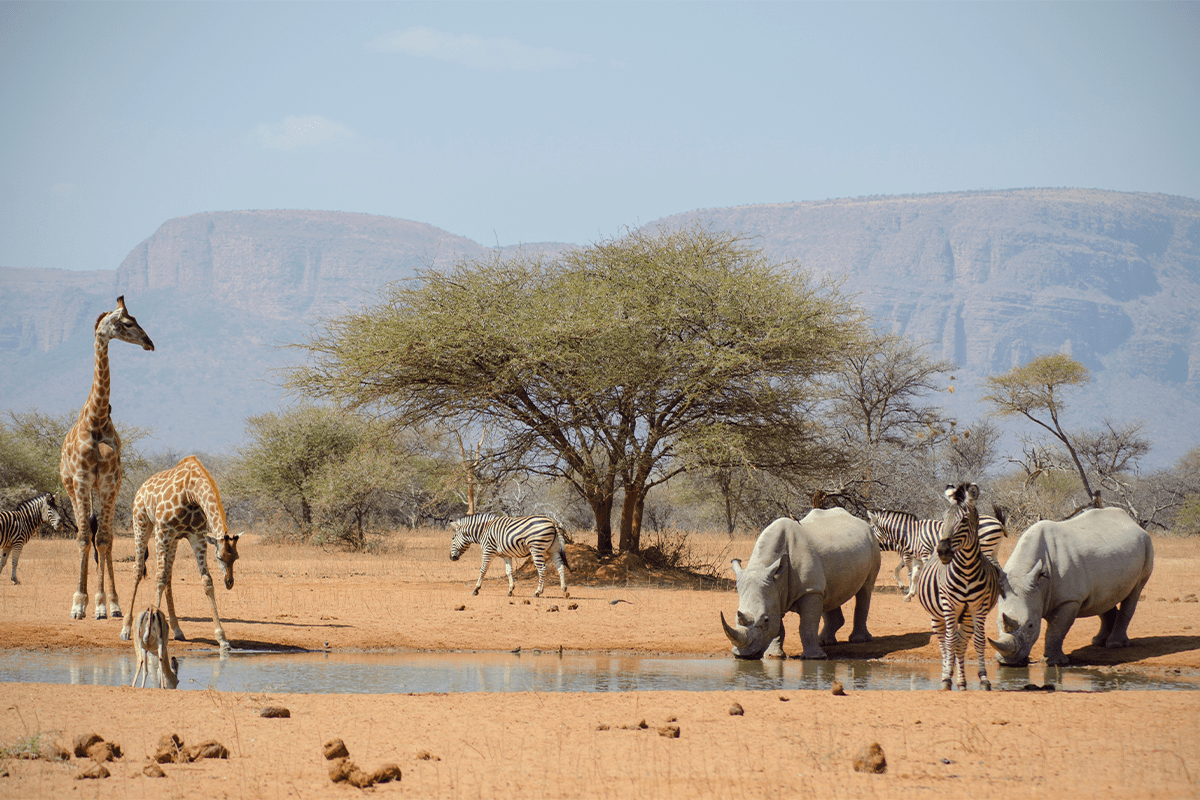
Safari landscape with giraffes, zebras, and rhinoceros, South Africa.
Ecosystem services
What do ecosystem services mean?
Ecosystem services refer to the benefits people derive from ecosystems, including both direct and indirect contributions to human wellbeing. These services can be thought of as the goods and services that ecosystems provide, such as food, clean water, and climate regulation, as well as the cultural, aesthetic, and spiritual values people associate with nature.
Types of ecosystem services
Ecosystem services can be classified into several types, including:
- provisioning services, such as the production of food, water, and other natural resources;
- regulating services, such as the regulation of climate, water quality, and disease;
- cultural services, such as the aesthetic, spiritual, and recreational benefits people derive from nature; and
- supporting services, such as nutrient cycling, soil formation, and photosynthesis.
Each of these ecosystem services plays an integral role in supporting human wellbeing and contributing to the overall functioning and health of ecosystems.
Read more: 10 Vital ecosystem services: sustaining life on Earth
The significance of ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are essential for human survival and wellbeing. They provide a wide range of benefits for economic, social, and environmental sustainability. Ecosystem services support food security by providing the crops, livestock, and fish we depend on for sustenance and also contribute to the development of medicines, energy, and other resources.
Ecosystem services also support human health by regulating the spread of disease, mitigating the impacts of natural disasters, and providing opportunities for recreation and relaxation. Finally, ecosystem services are critical for maintaining ecological processes that support the functioning of ecosystems and the Earth's biosphere. Protecting and maintaining ecosystem services is therefore a paramount priority for sustainable development.
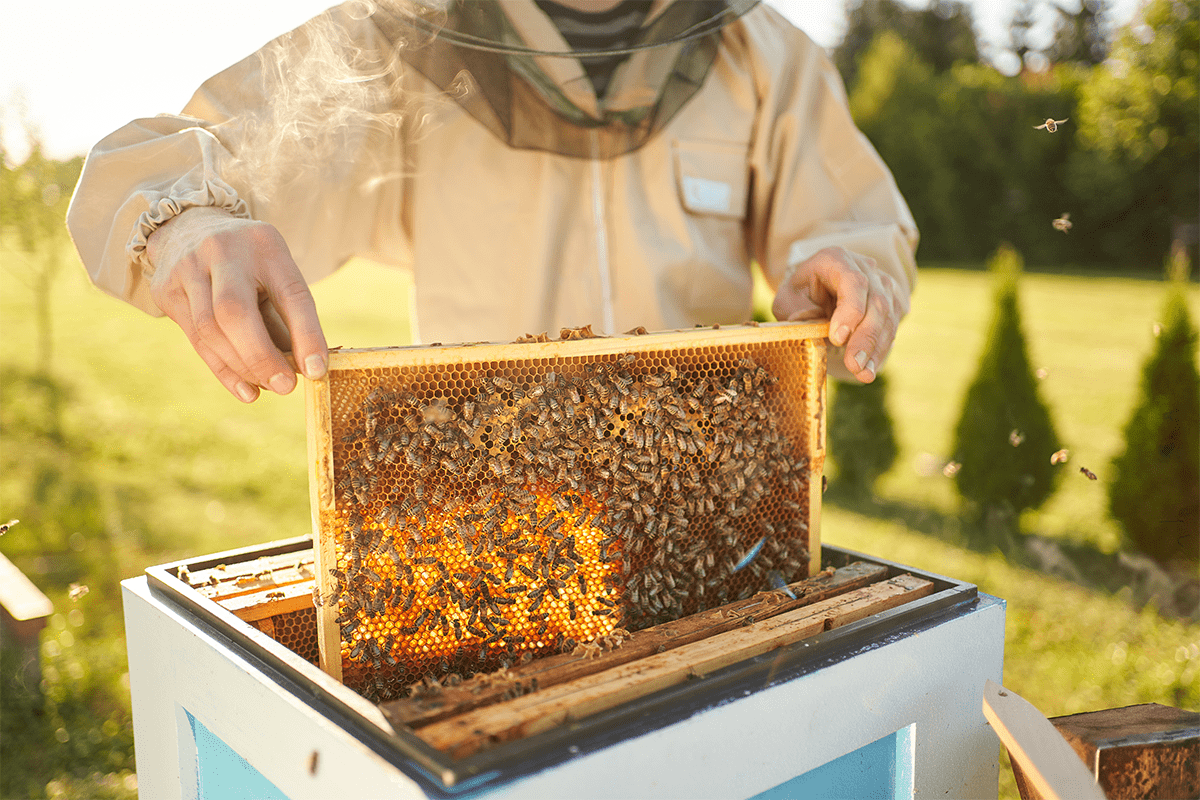

Beekeeper removing honeycomb from beehive.
Read more: Sweet solutions: the role of bees and Impact Investments in environmental restoration
The human impact on ecosystems
Overexploitation
Overexploitation refers to the unsustainable use of natural resources, such as overfishing, deforestation, and groundwater depletion. Human activities, such as intensive agriculture and logging, have led to the overexploitation of many ecosystems, resulting in biodiversity loss, soil degradation, and declining water quality. Overexploitation also has economic impacts, as it can lead to the depletion of resources that are critical for livelihoods and local economies.
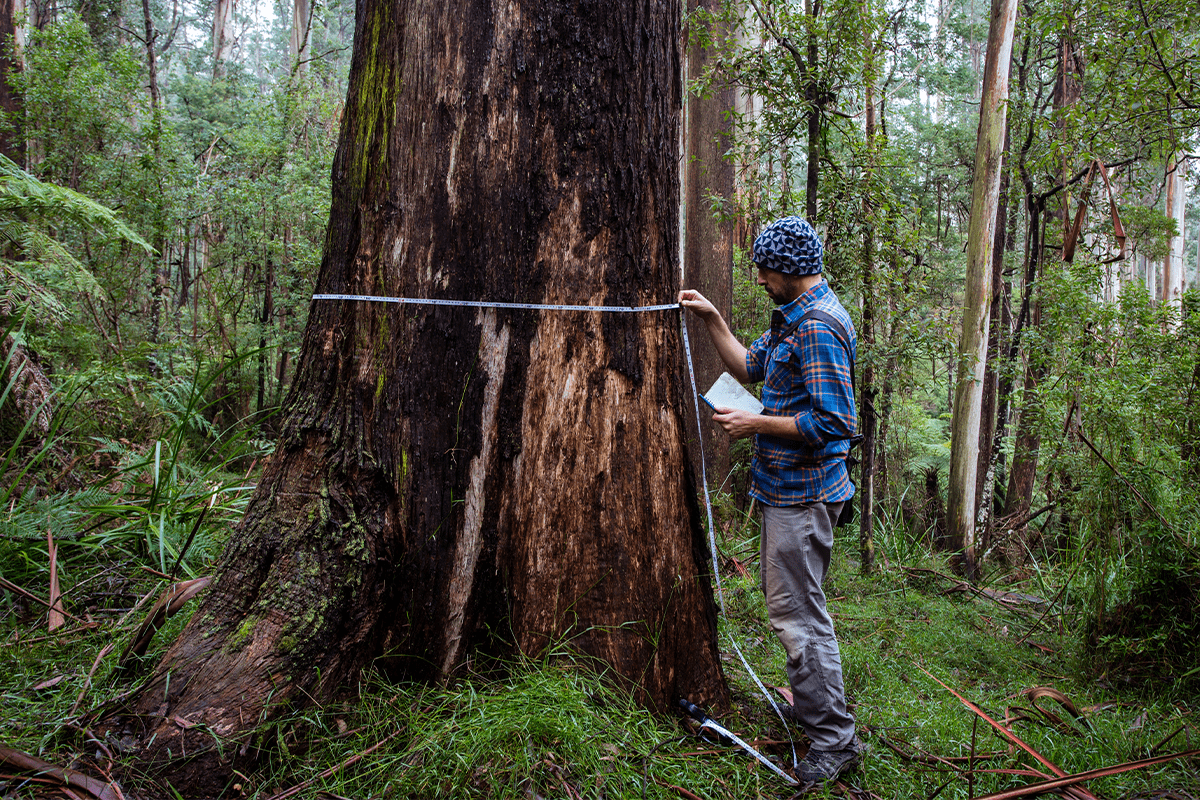

Tree researcher measuring a gum tree, Australia.
Pollution
Pollution is the release of harmful substances, such as chemicals, waste, and plastics, into the environment. Pollution has significant impacts on ecosystem health, including the contamination of water and soil, the destruction of habitats, and the loss of biodiversity. Pollution also has serious human health implications, including respiratory and neurological problems, and is a significant contributor to environmental instability.
Read more: The Science Based Targets initiative and carbon offsetting: striking the right balance
Environmental instability
Environmental instability refers to the disruption of the Earth's environmental and climate systems, which can significantly impact ecosystem health and functioning. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have led to a rapid increase in greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, causing the Earth's temperature to rise and leading to more frequent and severe weather events, such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes.
These changes can significantly impact ecosystem health, including changes in species distributions, the loss of habitats, and the decline of ecosystem services. Addressing environmental instability is therefore critical for protecting ecosystems and ensuring the sustainability of human societies.
Let us inform you
We will keep you updated on all the latest news.
Protecting our ecosystems
Conservation strategies
Conservation strategies aim to protect and preserve ecosystems. They include a range of measures, such as establishing protected areas, enforcing wildlife and habitat protection laws, and restoring degraded ecosystems. Conservation strategies often focus on preserving biodiversity and maintaining the ecological processes supporting ecosystem functioning. Conservation also involves promoting sustainable-use practices, such as responsible tourism, that support both ecosystem health and local economies.
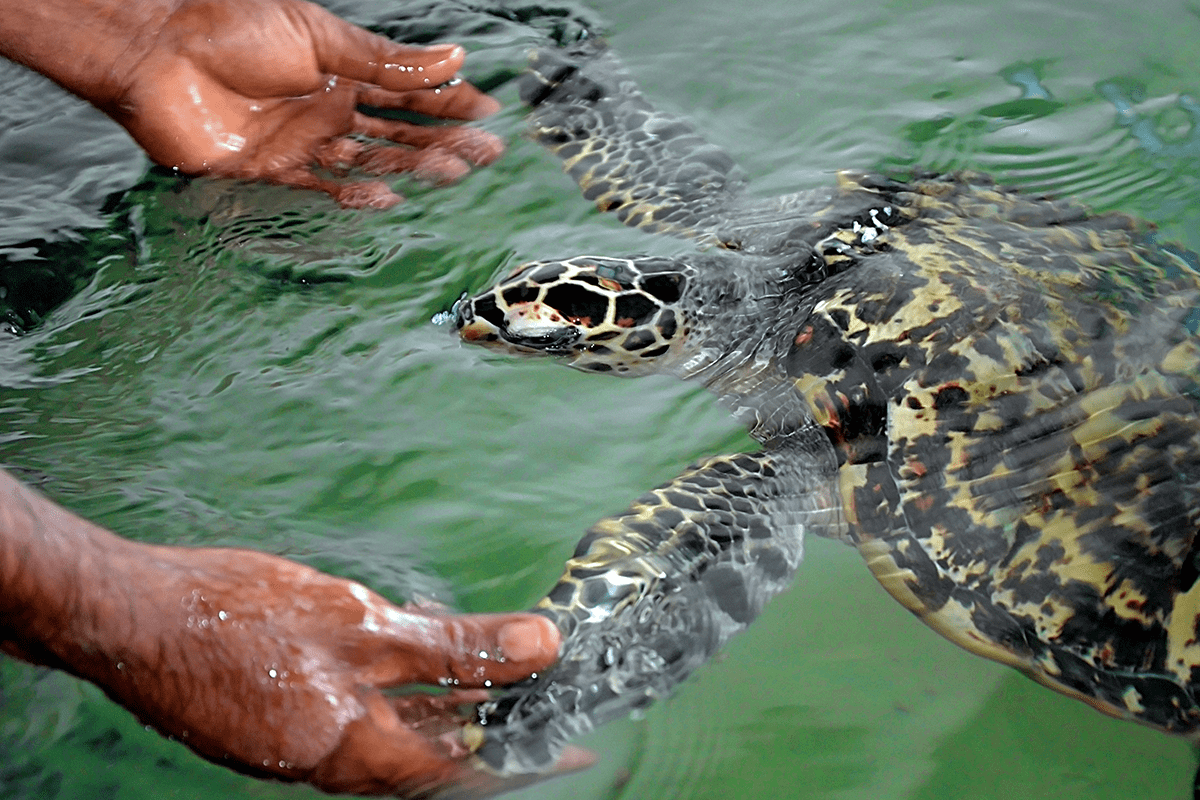

Rescued tortoise holding its flippers with human hands. The Sea Turtles Conservation Research Project in Bentota, Sri Lanka.
Find out more about Green Earth’s nature-based solutions
Restoration strategies
Restoration strategies aim to repair and restore degraded ecosystems to a more natural state. They include measures such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and the removal of invasive species. Restoration helps reverse the impacts of human activities, such as deforestation and pollution, and supports the recovery of ecosystem services and biodiversity. Restoration also has social and economic benefits, such as creating jobs and providing recreational opportunities.
Explore Green Earth’s nature-restoration projects
Sustainable-use strategies
Sustainable-use strategies involve the responsible use and management of natural resources, including wild and cultivated resources. It can include measures such as sustainable agriculture, fisheries management, and promoting renewable-energy sources. Sustainable-use strategies aim to support human wellbeing while minimising negative impacts on ecosystems and can be critical for the long-term conservation and protection of natural resources. Sustainable use can also support local economies and livelihoods and promote the equitable distribution of benefits from natural resource use.
Read more: Overcoming sustainability challenges: practical solutions for your business
Our projects
We develop large-scale, impactful projects.
Green Earth’s mission is interconnected with safeguarding ecosystems
Ecosystems are vital for human wellbeing and survival, providing a range of specific ecosystem services, such as clean water, food, and air, as well as supporting cultural and recreational values. Ecosystems also support biodiversity, providing habitats for millions of species and playing a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate and biogeochemical cycles.
However, ecosystems are facing significant threats from human activities, including overexploitation, pollution, and environmental instability, which are causing the loss of biodiversity, ecosystem functioning, and ecosystem services. Protecting and restoring ecosystems is therefore vital for maintaining human wellbeing and ensuring the sustainability of our planet.
Given the importance of ecosystems for human wellbeing and the significant threats facing them, we must take action to protect and restore them. We can do this with a range of measures, such as reducing our use of natural resources, promoting sustainable practices, and supporting conservation and restoration efforts.
At Green Earth, we are committed to supporting nature to flourish and prosper. We implement actionable strategies in support thereof with every project we undertake. We believe these efforts will benefit us all—and ensure that future generations will be given a chance to enjoy the wonders of nature as we do.
There are also individual actions each of us can take, like reducing our carbon footprint, supporting sustainable businesses, and advocating for policies that protect ecosystems. Protecting and restoring ecosystems is not only necessary for preserving biodiversity and supporting human wellbeing, but also for ensuring the sustainability of our planet and future generations. We all have a role to play in protecting ecosystems, and it is up to each of us to take action to secure a healthy future for ourselves and the planet.
The time to take action is now
.png?width=1200&height=800&name=Visual%20(41).png)
-1.jpg?width=1200&height=680&name=Frame%201%20(1)-1.jpg)




